Computed Axial Tomography (CAT) scan
Computed Axial Tomography (CAT) scan
Advanced medical imaging for accurate and confident diagnosis
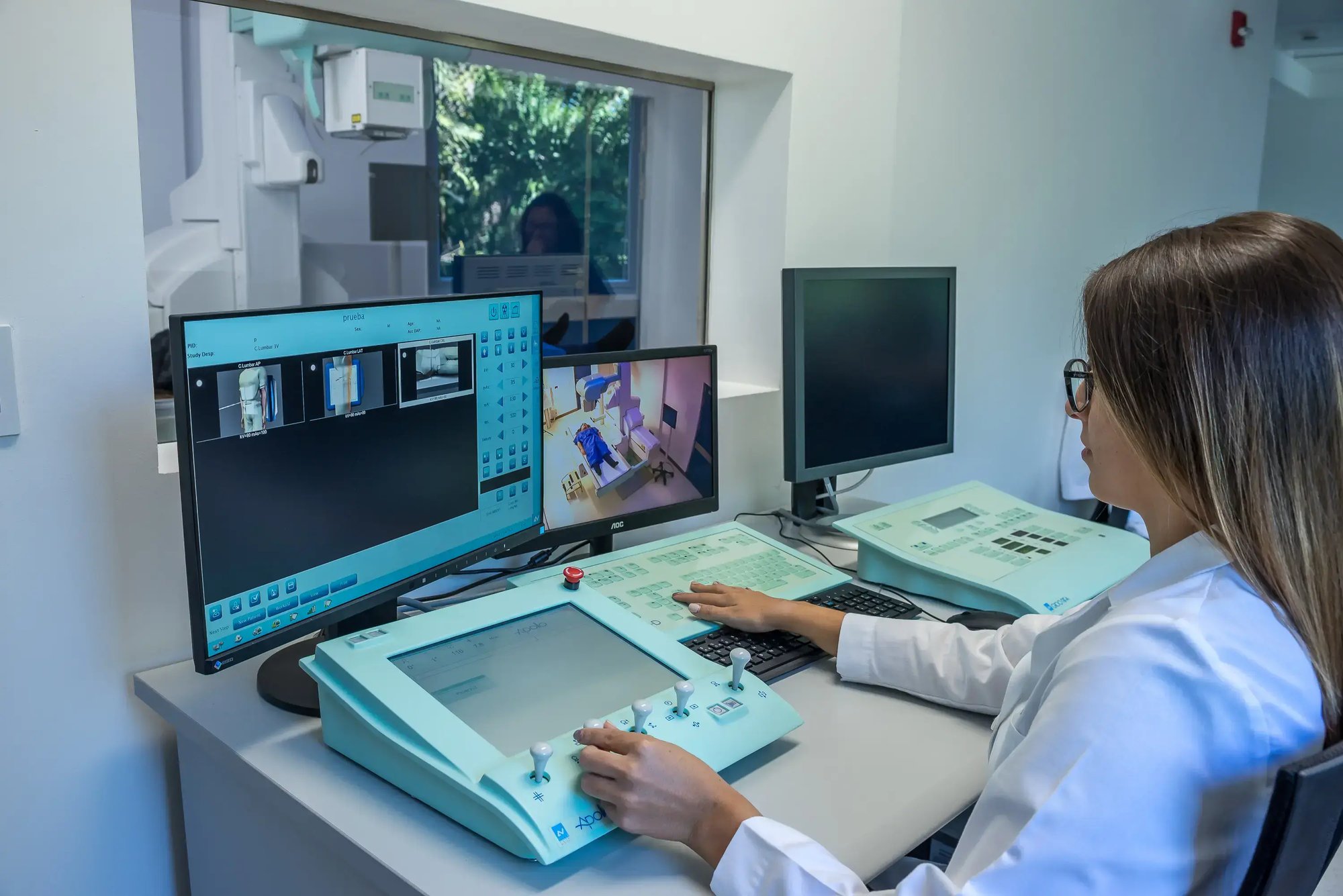
Computed Axial Tomography (CT) is a diagnostic imaging study that uses X-rays and computer processing to generate highly accurate cross-sectional slices of the body. These tomographic images make it possible to detect tumors, lesions, diseases or internal abnormalities in much greater detail than a conventional X-ray.
Thanks to its state-of-the-art technology, CT allows:
-
Three-dimensional reconstruction for better anatomical visualization.
-
Preventive studies such as CT Angiography and CT Pulmonary Analysis.
-
Evaluations without the need for sedation in pediatric or geriatric patients.
-
Optimized use of intravenous contrast medium, minimizing the dose thanks to the automatic synchronized injector.
What is CT used for?
CT is used to study multiple areas of the body: head, neck, thorax, abdomen, pelvis, extremities and spine. It is useful for:
-
Diagnosis of tumors
-
Detection of internal bleeding or fractures.
-
Evaluation of internal organs
-
Monitoring of chronic diseases
Types of CT scans
The studies can be performed: without contrast, with intravenous contrast and combined, according to medical indication.
The contrast improves the visibility of internal organs and structures, and its application is defined by the professional in the medical order.

 Telephone exchange
Telephone exchange

.webp?width=450&height=556&name=9R1A2622-Editar%20(1).webp)




.webp?width=1155&height=771&name=FLUROSCOPIA%20(12).webp)

.webp?width=1155&height=771&name=MAMOGRAFO%20(65).webp)

.webp)